Electricity doesn’t always come in the form we need. Devices require different types of current:
- AC (Alternating Current): Changes direction periodically; used in homes and power grids.
- DC (Direct Current): Flows in one direction; used in batteries, phones, and electronics.
Converting between these two forms is essential in electronics, and that’s where rectifiers and inverters come in.
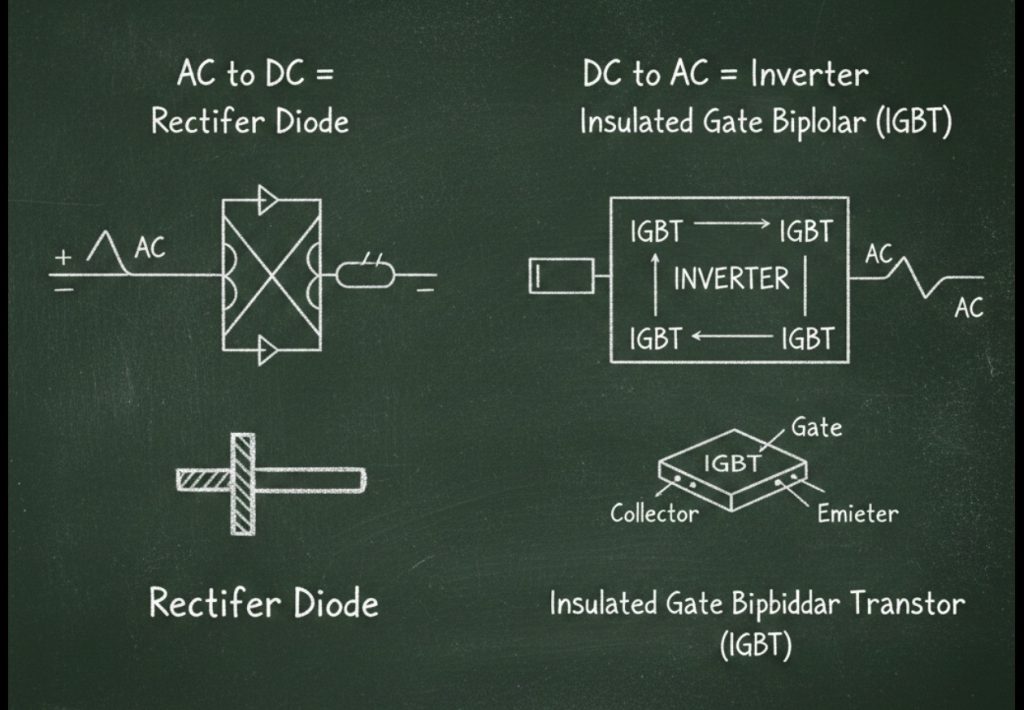
AC to DC: Rectifier
A rectifier converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC).
- Key Component:Diode
- A diode allows current to flow in only one direction, effectively “blocking” the reverse flow of AC.
Types of Rectifiers
- Half-Wave Rectifier: Uses one diode; only half of the AC waveform is converted.
- Full-Wave Rectifier: Uses multiple diodes; both halves of AC are converted for smoother DC output.
- Bridge Rectifier: Most common; uses four diodes in a bridge configuration for efficient full-wave rectification.
Applications:
- Phone chargers, adapters, LED drivers, power supplies.
DC to AC: Inverter
An inverter converts direct current (DC) back into alternating current (AC).
- Key Component:IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor)
- IGBTs act as high-speed electronic switches, turning DC on and off rapidly to produce AC.
- Offers high efficiency and precise control, ideal for large loads and renewable energy systems.
Types of Inverters
- Square Wave Inverter: Simple, low-cost, produces basic AC waveform.
- Sine Wave Inverter: Produces smooth AC, compatible with sensitive electronics.
- Modified Sine Wave Inverter: Intermediate, more efficient than square wave, cheaper than pure sine.
Applications:
- Solar power systems, UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply), electric vehicles, home appliances.
Fun Fact
- Rectifiers are the reason your phone battery charges from a wall plug—AC from the mains is converted to DC.
- Inverters are why solar panels or batteries can power your home appliances, which require AC.
- IGBTs are widely used in EVs and industrial drives because they handle high voltages and currents efficiently.
TL;DR
| Conversion | Component | Purpose | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC → DC | Diode (Rectifier) | Charge batteries, power electronics | Phone chargers, adapters, LED drivers |
| DC → AC | IGBT (Inverter) | Power AC devices from DC sources | Solar inverters, UPS, EVs |